CHỦ ĐỀ: GAN NHIỄM MỠ KHU TRÚ- GAN NHIỄM MỠ ĐA Ổ
PHẦN I: TÓM TẮT
PHẦN II: TẠM DỊCH
PHẦN I: TÓM TẮT:
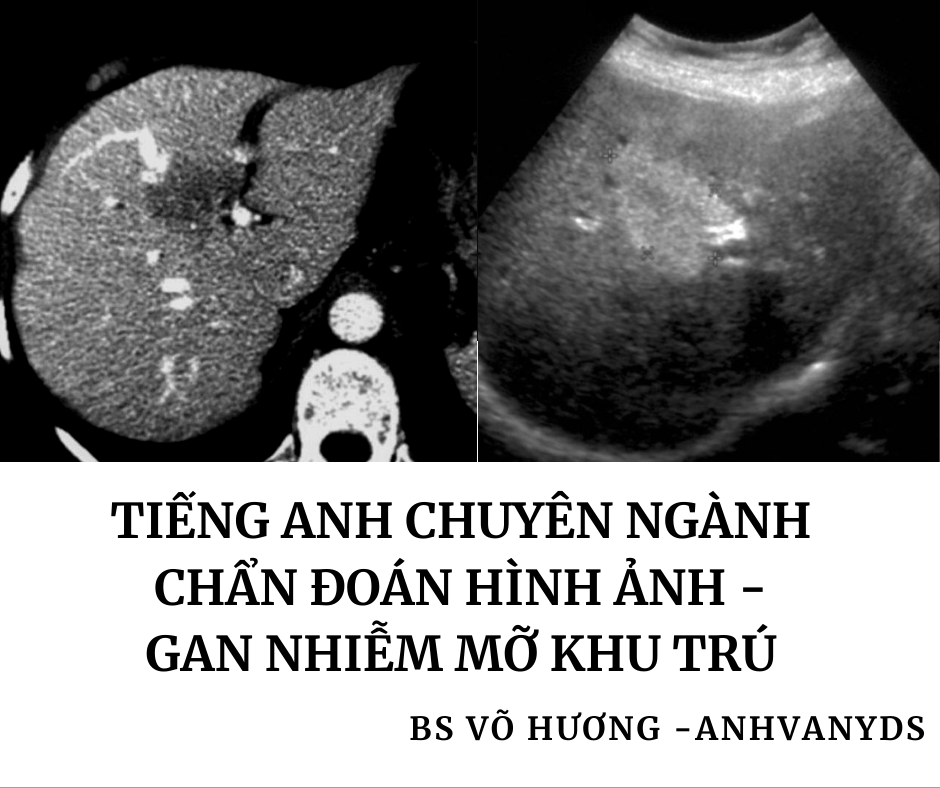
GAN NHIỄM MỠ KHU TRÚ (Focal hepatic steatosis)
CÁC ĐẶC ĐIỂM CHUNG (General features):
- Mức độ hút âm/tín hiệu(attenuation/signal) của vùng gan nhiễm mỡ khu trú chuyển sang của mỡ -> Mức độ hút âm (attenuation) gia tăng.
- Xuất hiện dưới dạng các vùng dạng bản đồ (geographic regions)
- Vị trí đặc trưng (characteristic locations): Hạ phân thùy IV(segment IV) gần cửa gan/rốn gan (the porta hepatis) HOẶC dây chằng liềm (the falciform ligament)
- Không có hiệu ứng khối (mass effect)
- Không có sự biến dạng của các mạch máu(distortion of vessels) chạy qua
CÁC ĐẶC ĐIỂM VỀ HÌNH ẢNH (RADIOLOGIC FEATURES):
Siêu âm:
Vùng nhiễm mỡ khu trú:
Có độ hồi âm tăng (increased echogenicity)
Mức độ hút âm (attenuation) gia tăng.
CT(Cắt lớp vi tính):
Vùng nhiễm mỡ khu trú : Giảm tỷ trọng (Decreased attenuation) ở hình ảnh trước tiêm thuốc/không tiêm thuốc (precontrast/ non-contrast) và hình ảnh sau tiêm thuốc thì tĩnh mạch cửa (portal venous phase imaging).
GAN NHIỄM MỠ ĐA Ổ (Multifocal hepatic steatosis )
ĐẶC ĐIỂM VỀ HÌNH ẢNH ( RADIOGRAPHIC FEATURES) :
Có nhiều ổ giống với vùng nhiễm mỡ khu trú trong gan
Khác nhau về kích thước từ vài mm đến vài cm.
Không có hiệu ứng khối (tức là chúng không đẩy lệch các mạch máu gan hoặc các cấu trúc khác) .
Không biểu hiện sự phân bố mạch máu bên trong (internal vascularity).
Ultrasound (Siêu âm)
Vùng hồi âm có giới hạn rõ (a well-circumscribed area of echogenicity).
Có thể có bóng lưng /bóng cản âm (Acoustic shadowing).
Doppler màu: không có hoàn toàn hoặc chỉ có dòng chảy (flow) nhẹ vùng gan nhiễm mỡ .
CT( cắt lớp vi tính)
Tổn thương tỷ trọng thấp (a low density lesion)
Không có (sự ngấm thuốc/tương phản) (rõ rệt/có thể nhìn thấy) (visible enhancement) .
PHẦN II: TẠM DỊCH
GAN NHIỄM MỠ KHU TRÚ (Focal hepatic steatosis)
Definition:
Focal hepatic steatosis, also known as focal fatty infiltration, represents small areas of liver steatosis. In many cases, the phenomenon is believed to be related to the hemodynamics of a third inflow.
Third inflow refers to anatomical variants leading to an additional venous inflow to the liver apart from the usual dual blood supply (portal vein and hepatic artery). They tend to be associated with parenchymal pseudolesions (focal hyperenhancement on post-contrast imaging, focal fat infiltration, or focal fat sparing) and, therefore, the recognition of these variant liver hemodynamics is crucial. Potential anatomic variations include:
Aberrant right gastric venous drainage (dẫn lưu tĩnh mạch dạ dày phải bất thường):
- reported prevalence is up to 49% of the population (tỷ lệ hiện mắc được báo cáo lên đến 49% dân số)
- can lead to hepatic pseudolesions in the posterior segment IV (có thể dẫn đến các giả tổn thương gan ở sau HPT IV)
Epigastric-paraumbilical veins (các tĩnh mạch thượng vị- quanh rốn)
- venous blood flow from the abdominal wall to the liver (dòng máu tĩnh mạch từ thành bụng đến gan): superior and inferior veins of Sappey (tĩnh mạch trên và dưới của Sappey), vein of Burow (tĩnh mạch của Burow)
- hepatic pseudolesions near the falciform ligament (Các giả tổn thương gan gần dây chằng liềm).
Cholecystic veins (tĩnh mạch túi mật)
- can lead to hepatic pseudolesions in the posterior segment IV and V (có thể dẫn đến các giả tổn thương gan ở sau HPT IV và V)
Aberrant left gastric venous drainage (dẫn lưu tĩnh mạch dạ dày trái bất thường)
- around 4% of the population (khoảng 4% dân số )
- can lead to hepatic pseudolesions in the posterior segment II and III (có thể dẫn đến các giả tổn thương gan sau HPT II và III).
Pathology (Bệnh học)
Location(Vị trí)
A characteristic location for focal fatty change is the medial segment of the left lobe of the liver (segment IV) either anterior to the porta hepatis or adjacent to the falciform ligament. This distribution is the same as that seen in focal fatty sparing and is thought to relate to variations in vascular supply. This also would account for focal fatty change/sparing sometimes seen related to vascular lesions.
Radiographic features (Những đặc điểm về hình ảnh)
Ultrasound (Siêu âm)
Ultrasound features only become apparent when the amount of fat reaches 15-20%. Features include:
- increased hepatic echogenicity: tăng độ hồi âm gan
- hyperattenuation of the beam: tăng mức độ hút âm của chùm tia
- mild or absent positive mass effect: hiệu ứng khối không có hoặc nhẹ
- geographic borders: ranh giới/bờ dạng bản đồ.
- no distortion of vessels: không có sự biến dạng của các mạch máu.
- inability to visualize the portal vein walls (as the parenchyma is as bright as the wall)
- không có khả năng thấy các thành tĩnh mạch cửa (vì nhu mô sáng bằng thành)
CT(Cắt lớp vi tính)
decreased attenuation (non-contrast CT): giảm tỷ trọng (CT không tiêm thuốc cản quang)
normal liver 50-57 HU: gan bình thường: 50-75HU)
decreases by 1.6 HU per mg of fat in each gram of liver (giảm mỗi 1,6 HU trên mỗi mg chất béo trong mỗi gam của gan)
decreased attenuation (post-contrast CT): giảm tỷ trọng (CT sau tiêm thuốc cản quang)
liver and spleen should normally be similar on delayed (70 seconds) scans:
earlier scans are unreliable as the spleen enhances earlier than the liver (systemic supply rather than portal).
Differential diagnosis (Chẩn đoán phân biệt)
When located in characteristic locations then there is usually little difficulty in making the correct diagnosis. If unusual in location or appearance then differentials to be considered include:
Hepatic hemangioma (u máu gan):
the commonest hyperechoic liver lesion, typically well defined and may show peripheral feeding vessels
- hepatic abscess: áp xe gan
- liver neoplasms: khối u gan
- primary liver tumors: khối u gan nguyên phát
- hepatic metastases: di căn gan
GAN NHIỄM MỠ ĐA Ổ(Multifocal hepatic steatosis)
Definition
Multifocal hepatic steatosis (also known as multifocal nodular hepatic steatosis) is the uncommon finding of multiple foci of focal fat in the liver mimicking – and at times being confused with – hepatic metastases.
Clinical presentation (Bối cảnh/bệnh cảnh lâm sàng)
Multifocal hepatic steatosis is usually an incidental imaging finding.
Radiographic features (Đặc điểm về hình ảnh)
The steatotic lesions vary from several millimeters to centimeters in size. They lack mass effect (i.e. they do not displace hepatic vessels or other structures) and display no internal vascularity.
Ultrasound (Siêu âm)
Focal steatosis on ultrasound usually forms a well-circumscribed area of echogenicity without mass effect. Acoustic shadowing may be present. Using color Doppler usually shows a complete absence, or only slight flow, within the affected liver .
CT( cắt lớp vi tính)
Focal steatosis on CT usually forms a low density lesion without mass effect or visible enhancement.
Nguồn:
https://radiopaedia.org/articles/multifocal-hepatic-steatosis?lang=us
https://radiopaedia.org/articles/focal-hepatic-steatosis?lang=us.
Bs Võ Hương – Anhvanyds.
Để lại một phản hồi Hủy